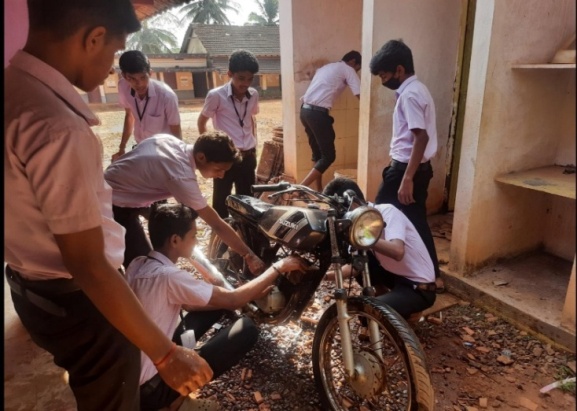
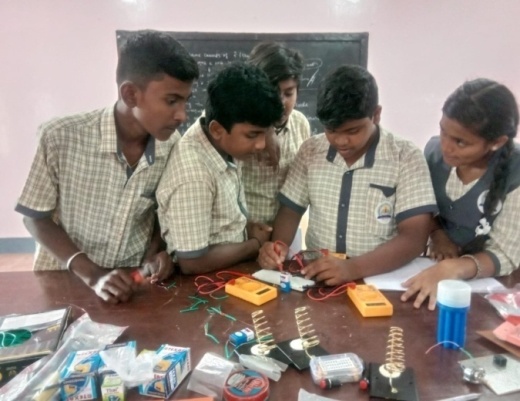
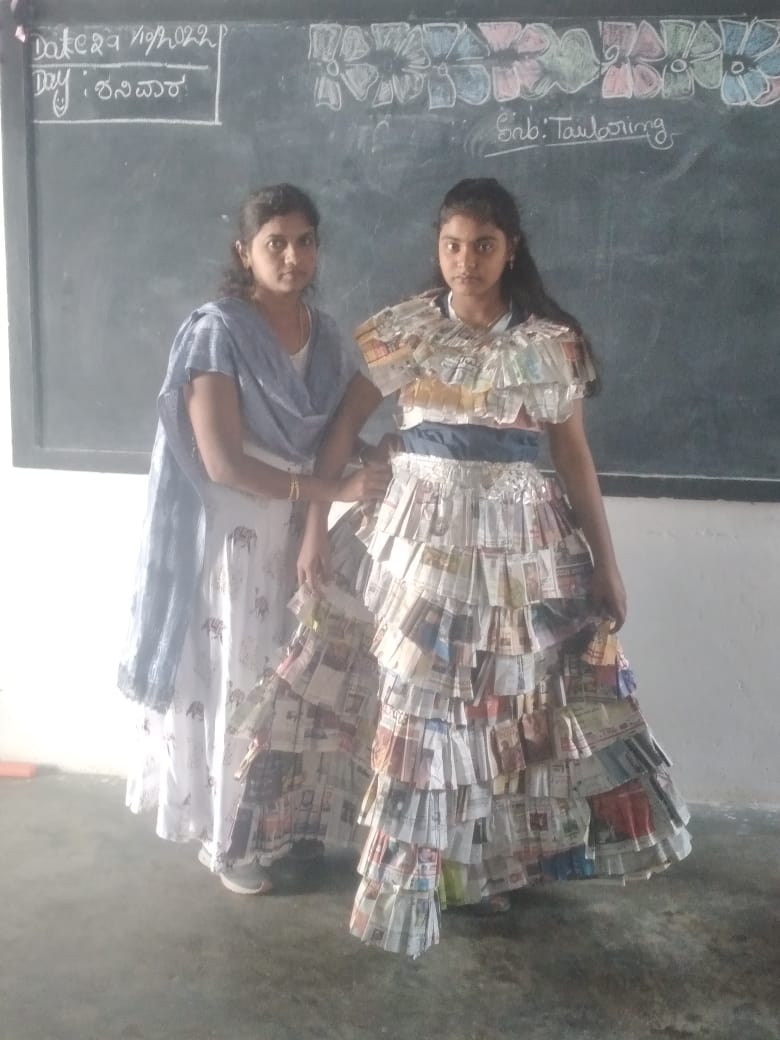
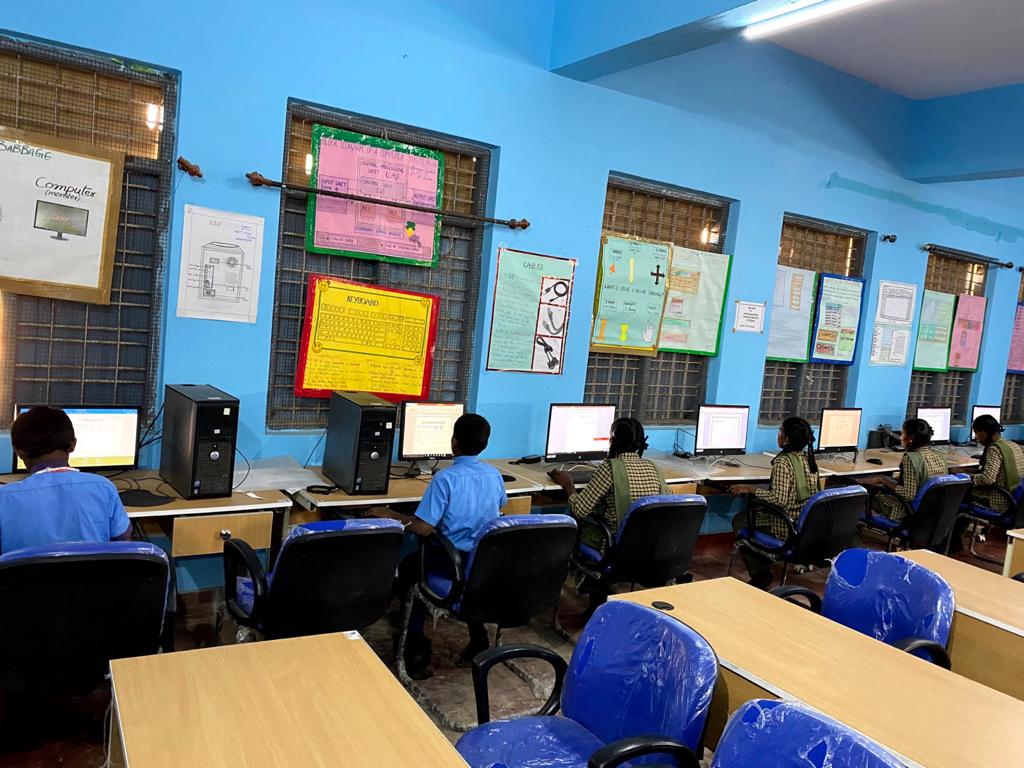
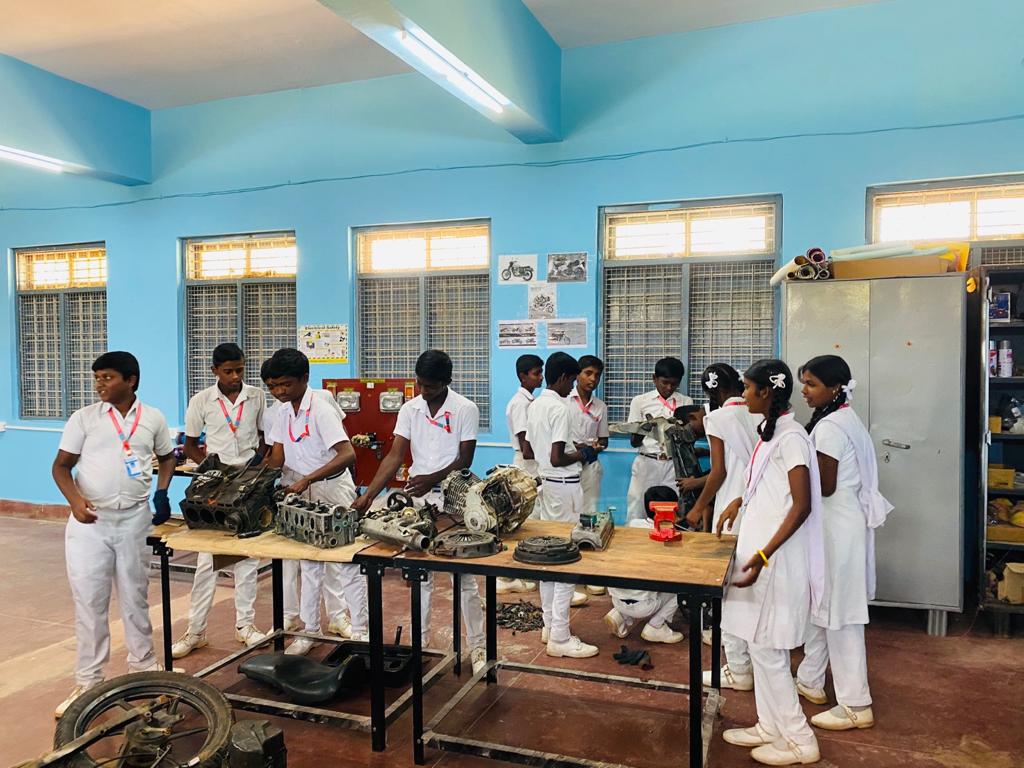
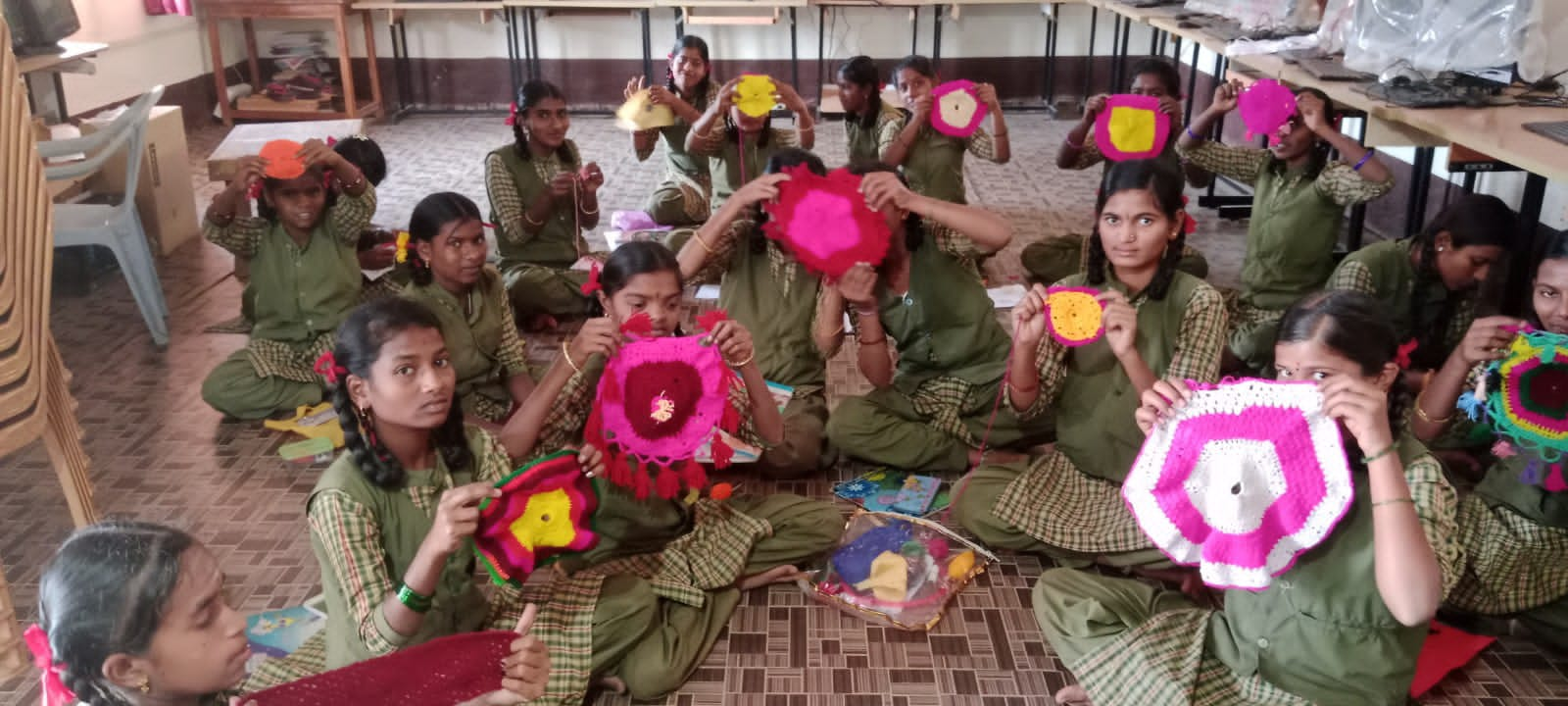
Skilling should predominantly be a thrust area in the immediate future. To enable our students develop aptitude towards skilling Ministry of Education started to introduce vocational education right from Secondary Stage. The centrally sponsored scheme of Vocationalisation of secondary and higher secondary education approved by the Government of India in September 2011 has been revised on 12th February 2014 with a view to align it with the National Skills Qualification Frame Work. The scheme covers Vocational education from level 1 to level 10 starting from class 9th to PhD.
National Skill Qualification Framework
The NSQF project was approved for the in the year 2012-13, implemented in 2013-14 and made functional from the academic year 2014-15 in Karnataka. The National Skills Qualifications Framework (NSQF) established in the year 2012-13 organizes qualifications according to a series of levels of knowledge, skills and aptitude. These levels are defined in terms of learning outcomes which the learner must possess regardless of whether they were acquired through formal, non-formal or informal learning.
In that sense, NSQF is a quality assurance framework. It is, therefore, a nationally integrated education and competency based skill framework that will provide for multiple pathways, horizontal as well as vertical, both within vocational education and vocational training, general education and technical education, thus linking one level of learning to another higher level. This will enable a person to acquire desired competency levels, transit to the job market and, at an opportune time, return for acquiring additional skills to further upgrade their competencies.
The GOI has brought out a revised centrally sponsored scheme of Vocationalisation of secondary & Higher Secondary education by integrating employability, education into school education. The scheme is operated within the National Skill Qualification Frame work which establishes a system of clear educational pathways from school to Higher education while providing certification of vocational skills. The project has been approved for the State of Karnataka, MHRD, GOI & accordingly Karnataka is implementing the NSQF from the academic year 2014.
- Design of NSQF:
- Each school will have 01 trainer for each sector.
- It is now implemented in 375 government schools spread all over the State.
- It is a voluntary scheme for students studying in various Government schools of Karnataka.
- The students of 9th & 10th std who have opted NSQF subject are exempted in studying 03rd language. G.O:ED.59.MCD.2016, Dated:16-06-2016
- The students of 11th & 12th std who have opted NSQF subject are exempted from studying either one of the languages. G.O:ED.59.MCD.2016, Dated:16-06-2016
- KSEAB to conduct annual theory examination for 9th & 10th std & Pre-university Education to conduct examination for 11th & 12th std.
- Practical assessments are conducted jointly by concerned Sector Skill Councils & concerned examination board.
- A joint certificate for students who pass out of 10th & 12th std are provided with Joint certification from respective SSCs & concerned examination boards.
- 198 schools with 2 sectors and 69 schools with single sector.
- Since 2018-19 students have been provided joint certification.
Aims of NSQF
- The major aim of introducing vocational education at secondary level and higher secondary level is to enhance the employability of youth through demand driven competency based, modular vocational courses and at the same time reduce the dropout rate at the secondary level.
- The national policy planners have considered secondary and higher secondary stage of school education as crucial, since at these stages the necessary skills and competencies are acquired which enable the students to enter the world of work to go for higher education.
- In the existing general education, emphasis is not given for technical skills or job oriented skills. If India wants to have a competitive advantage, it is very much necessary to introduce vocational education and training, integrated with general education which will help to create skilled workforce for the Country.
- The relevance of the vocational education has increased in the fast growing Indian economy, especially in the light of the governments thrust on universalisation of secondary education. Skill development and social justice through inclusive education and training in Vocational education has also been accorded high priority in the NEP 2020, which states “The introduction of systematic, well planned and rigorously implemented program of vocational education is crucial in the proposed education reorganization”
- NEP 2020 also recommends that “By 2025, at least 50% of learners through the school and higher education system shall have exposure to vocational education,
for which a clear action plan with targets and timelines will be developed.Vocational
education will be integrated into all schools and higher education Institutions in a
phased manner over the next decade”.
- f) It is the aim of NSQF to provide Vocational Education to 50% of the students, either
directly or at least through Vocational Exposure.
- Scope
The scope of NSQF is very vast as it covers all walks of endeavor; a student has to cross throughout his student carrier.
- Objectives of NSQF:
- The main objective of this project is to ensure that Karnataka succeeds in rolling out Vocational education under NSQF starting with 9th class going up to class 12th & meeting the aspiration of all stake holders and thus reduce dropouts.
- Successfully introduce and integrate NSQF courses at the Class 9th – 12th (in the 14-17 years age group) on an optional/voluntary basis in all schools of Karnataka.
- NSQF project will formalize the trainings as per National Occupational Standards (NOS) and standardize the outcome of the trainings, i.e. quality of students with respect to both technical skills as well as work readiness for the entry level job roles in the relevant sector at the end of Level 4.
- Post Level 4, as students have the options to go for employment or continue the studies. main objective is to improve employability skills in students.
- Ensure the employability of youth through demand driven competency based modular vocational courses
- Maintain their competitiveness through provisions of multi-entry multi-exit learning opportunities and vertical mobility/interchangeability in qualifications.
- Fill the gap between educated and employable.
- Specific outcomes expected from implementation of NSQF:
- The major expected outcome is reduction in school dropout rates & better attendance levels due to better job prospects ,
- Mobility between vocational and general education by alignment of degrees with NSQF
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL), which allows transition from non-formal to organized job market.
- Standardized, consistent, nationally acceptable outcomes of training across the country through a National Quality Assurance Framework.
- Global mobility of skilled workforce from India, through international equivalence of NSQF.
- Mapping of progression pathways within sectors and cross-sector ally.
- The courses selected are industry driven based on National Occupational Standards. This project is expected to improve employability of the students passing from these courses because of industry driven inputs & exposure.
- The project will be jointly funded by Central & State Government.
Status of implementation:
The project was approved for the State of Karnataka in the year 2012-13, but was implemented in 2013-14. But made functional from the academic year 2014-15. This project was introduced in selected 100 Composite Government Schools in Karnataka with an aim to prepare students for employability, once they complete of Higher Secondary Education, though they are always encouraged to study further. MHRD sanctioned another 50 schools in the year 2018-19, raising the total NSQF implemented schools to 150 in Karnataka. The PAB did not approve any schools in the year 2019-20.In the year 2020-21 PAB approved 53 schools and in 21-22 it approved 37 schools. The total number of schools implementing NSQF came to 240. In the year 2022-23, 35 schools were again approved bringing the total number of schools implementing NSQF to 275. Additional 100 schools along with 9 spoke schools were approved in the year 2023-24 bringing the total of 375 schools and 9 spoke schools. Among these 375 schools 198 schools are implementing 2 sectors and 169 schools are implementing 1 sector.
In the year 2024-25, 35 spoke schools, 100 additional schools and 8 KGBV Type 3 schools were approved by PAB bringing the total schools Implementing Vocational Education to 527. As a new juncture 123 secondary schools were approved under PM SHRI schools with its flagship programme under Ministry of Education Government of India.
In Position Teachers
Number of trainers deployed based on implemented sectors and in Schools in 2024-25
|
Sl. No
|
Sector
|
No of Sectors
|
|
01
|
IT / ITES
|
245
|
|
02
|
Automobile
|
192
|
|
03
|
Beauty & Wellness
|
165
|
|
04
|
Retail
|
34
|
|
05
|
Electronics and Hardware
|
67
|
|
06
|
Apparels made-ups and home furnishing
|
81
|
|
|
Total
|
784
|
| |
|
|
|
Schools level activities
- Sector wise enrolment of Students:
|
Sectors
|
Class 9th
|
Class 10th
|
Class 11th
|
Class 12th
|
Total
|
Total
|
|
Girls
|
Boys
|
Girls
|
Boys
|
Girls
|
Boys
|
Girls
|
Boys
|
Girls
|
Boys
|
|
|
IT / ITEs
|
1124
|
1646
|
1087
|
1496
|
807
|
1231
|
548
|
1097
|
5470
|
3566
|
4415
|
|
Automobile
|
595
|
3430
|
444
|
2794
|
212
|
1850
|
112
|
1125
|
1363
|
9199
|
10562
|
|
Beauty & Wellness
|
2470
|
442
|
1892
|
138
|
1247
|
10
|
781
|
0
|
6390
|
290
|
6680
|
|
Retail
|
245
|
235
|
187
|
172
|
170
|
50
|
123
|
29
|
725
|
486
|
1211
|
|
Apparels made-ups and home furnishing
|
842
|
181
|
646
|
79
|
79
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1567
|
260
|
1827
|
|
Electronics and Hardware
|
399
|
726
|
294
|
584
|
45
|
55
|
0
|
0
|
738
|
1365
|
2103
|
|
Total
|
6510
|
5880
|
5082
|
4806
|
3257
|
2866
|
2174
|
1782
|
17023
|
15334
|
32357
|
- The result analysis is the basis for every year activities. The analysis for the year 2023-24 is as follows
|
Sl No
|
Sector
|
10TH STD
|
12TH STD
|
TOTAL
|
|
<35
|
>36 <50
|
>51 <60
|
>61 <85
|
>86
|
Total
|
<35
|
>35 <50
|
>50 <60
|
>60 <85
|
>86
|
Total
|
<35
|
>35 <50
|
>50 <60
|
>60 <85
|
<85
|
Total
|
|
1
|
Information Technology
|
19
|
67
|
130
|
1353
|
878
|
2498
|
6
|
29
|
47
|
609
|
849
|
1608
|
25
|
96
|
177
|
1962
|
1727
|
4106
|
|
2
|
Automobile
|
10
|
58
|
152
|
1539
|
914
|
2728
|
15
|
16
|
68
|
467
|
379
|
935
|
25
|
74
|
220
|
2006
|
1293
|
3663
|
|
3
|
Beauty & Wellness
|
1
|
9
|
53
|
909
|
769
|
1744
|
1
|
0
|
9
|
204
|
378
|
599
|
2
|
9
|
62
|
1113
|
1147
|
2343
|
|
4
|
Retail
|
1
|
1
|
19
|
164
|
155
|
345
|
0
|
3
|
3
|
46
|
49
|
101
|
1
|
4
|
22
|
210
|
204
|
446
|
|
5
|
Electronics
|
0
|
10
|
11
|
359
|
211
|
592
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
10
|
11
|
359
|
211
|
592
|
|
6
|
Apparels
|
0
|
6
|
18
|
366
|
157
|
547
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
6
|
18
|
366
|
157
|
547
|
|
Total
|
31
|
151
|
383
|
4690
|
3084
|
8454
|
22
|
48
|
127
|
1326
|
1655
|
3243
|
53
|
199
|
510
|
6016
|
4739
|
11697
|
- Motivation camps in schools:
To make students realize the importance of vocational education and motivate them to pursue their dream career options, motivation camp is the first activity that will be conducted by trainers in their respective schools. Our own trainers conduct Motivation Camps not only in their schools but also in various new schools to handhold the new trainers and stakeholders in their respective districts, in order to create awareness regarding Vocational Education.
- Field visits and Guest lecturer:
Every trainer in the schools is supposed to conduct 2 field visits to provide Hands on Experience in an industrial atmosphere, in their individual sector along with conducting 4 Guest lectures. These guest lecturers help the students in acquiring information on various aspects with relevance to their sectors. Resource Persons from various fields are invited to each school to provide these lectures.
- Raw material Grant for Schools:
School Grants for purchase of raw materials, Maintenance of Tools and Equipments, Photocopies of Books and study materials for vocational education in schools in accordance with the sectors are provided to implemented schools. Grants for payment of Electricity & water charges will also be released to schools along with grants to purchase of necessary stationery.
- Establishment of Vocational Cell:
A vocational Cell has been established in Samagra shikshana as per GO No.EP76 yosaka 2021 Bengalure. Dated:25-03-2021 with representatives from NSDC and KSDC
- Training of trainers(ToT)
- Induction training:
Induction training was conducted to 150 New trainers who have joined our NSQF team. The Schedule of the same is as follows.
- Training of trainers regarding Soft Skills:
An online training in English language and 21st century skills by “MACMILLAN PUBLISHERS INDIA PRIVATE LIMITED”.a 11 day programme was organized as a joint venture by Karnataka State Skill Development Corporation and Samagra Shikshana Karnataka in 2 batches. The training included various aspects of 21st century skills, like problem solving Green skills.etc.
- Skill based In service training:
Various Skill based in-service training programme both offline and online will be organized for all sector trainers both by PSSCIVE Bhopal and also SSK.
Practical assessment of students will be conducted by respective Sector Skill Councils where as Theory exams will be conducted by Karnataka State Examination and Assessment Boards.
- Certification of students:
Students will be issued Joint certification both by the respective boards and concerned Sector Skill Councils, which is an added factor to all the students perusing NSQF.
- Pre-Vocational Education:
- Exposure to vocational Education: All the students from std 6th onwards of NSQF implemented Schools are provided exposure to vocational education through a unique programme called Project Innovation.
- During 2021-22 Project Innovation was implemented in 150 NSQF providing exposure to around 450 students from class 6th
During 2024-25 the same programe was extended to 474 NSQF implemented schools along with 71 KGBVs and 5 NSBAVs across the state.